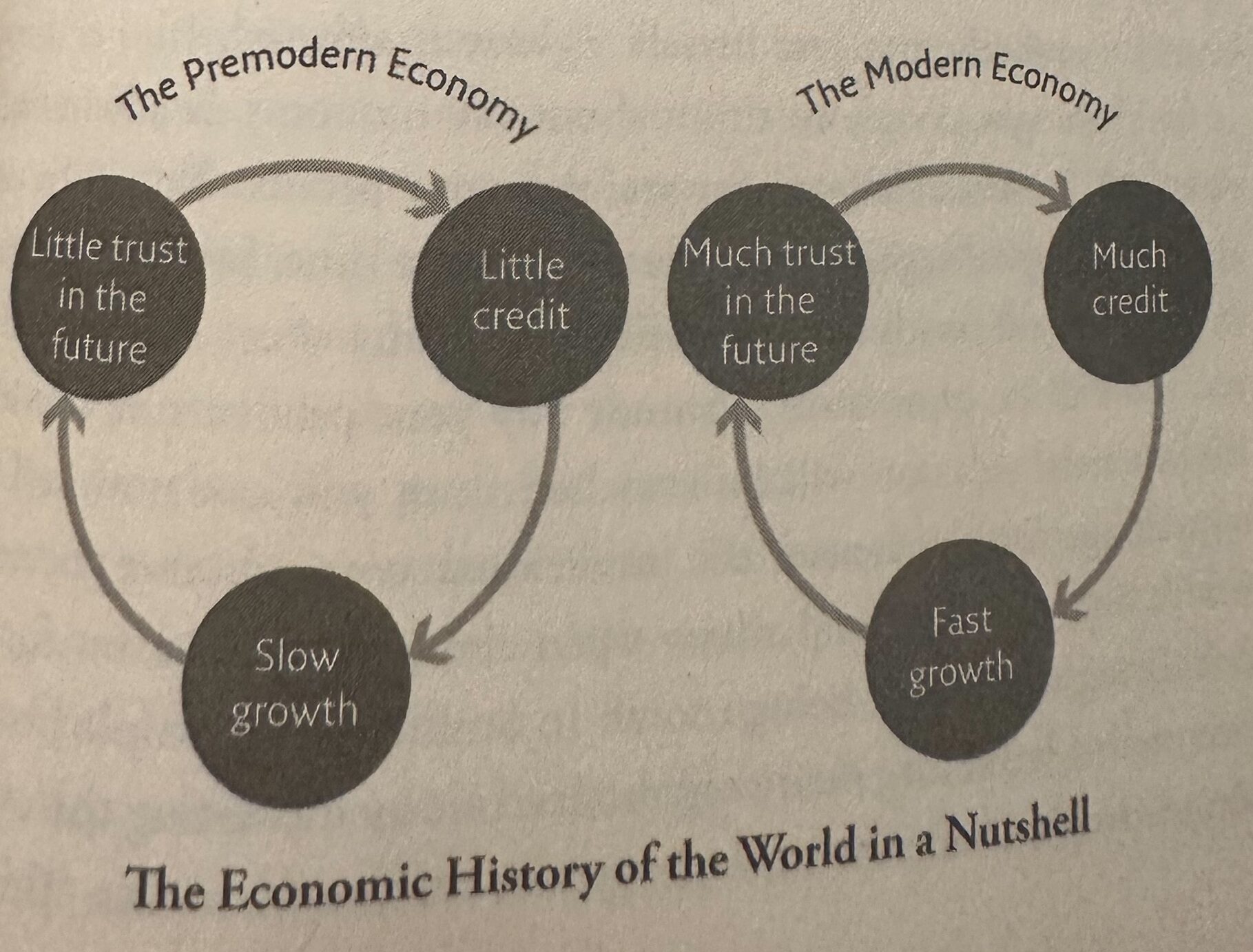
An economy without credit would look significantly different from the modern economies we are familiar with today. Credit plays a central role in many aspects of economic activity, and its absence would have profound effects. Here are some key ways in which an economy without credit would differ:
- Limited Capital Formation: Without access to credit, individuals and businesses would have to rely solely on their savings or equity to make investments or start new ventures. This would significantly limit the capacity for capital formation, which is essential for economic growth. Businesses would find it harder to expand, innovate, or launch new products, and this could hinder overall economic development.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Consumer credit, such as credit cards and personal loans, enables individuals to make purchases beyond their immediate means. Without such credit, people would need to save money before making significant purchases, leading to a reduction in consumer spending. This could lead to decreased demand for goods and services, potentially slowing down economic activity.
- Impact on Homeownership: Real estate transactions often rely on mortgage loans. Without access to mortgages, homeownership rates might decline, and it could become more challenging for people to buy homes. This could affect the housing market and related industries.
- Business Operations: Many businesses rely on credit to finance their day-to-day operations. Without lines of credit or business loans, some companies might struggle to manage cash flow, pay employees, or purchase inventory. This could lead to more volatile business cycles and potential bankruptcies.
- Job Creation: The availability of credit can influence job creation. Start-ups and small businesses often depend on loans to hire employees and expand their operations. A lack of credit may limit job opportunities and economic mobility.
- Monetary Policy Challenges: Central banks often use interest rates to influence the availability of credit. In an economy without credit, the tools available to central banks for managing monetary policy would be limited. They would need to rely more heavily on other tools, such as adjusting money supply, to control inflation and stimulate economic growth.
- Financial Services Industry: The financial services sector, including banks, credit unions, and fintech companies, would look very different without credit-related products and services. These institutions would need to adapt or focus on other financial services.
It’s important to note that the absence of credit does not mean the absence of financial transactions or lending altogether. Barter systems, alternative financial arrangements, and equity-based investments might replace traditional credit to some extent. However, these alternative mechanisms come with their own challenges and limitations.
In summary, an economy without credit would likely experience reduced economic growth, limited access to capital for businesses and individuals, lower consumer spending, and potential disruptions in various industries. Credit is a fundamental driver of economic activity in modern economies, and its absence would have far-reaching consequences.



